Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sc
Sc )
) O
O determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction
determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction田中 誠也*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; 石川 喜久*; 天児 寧*; 飯山 拓*; 二村 竜祐*; 丸山 建一*; 内海 重宣*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014403_1 - 014403_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sc-substituted hexagonal ferrite Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O has an incommensurate helimagnetic structure. However, the incommensurate helimagnetic structure has not been sufficiently determined, and the mechanism via which the helimagnetism develops has not been studied. Time-of-flight single-crystal neutron diffraction measurements were performed on single-crystal samples of Ba(Fe
has an incommensurate helimagnetic structure. However, the incommensurate helimagnetic structure has not been sufficiently determined, and the mechanism via which the helimagnetism develops has not been studied. Time-of-flight single-crystal neutron diffraction measurements were performed on single-crystal samples of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O with Sc concentrations of x = 0, 0.128, 0.153, and 0.193. The magnetic structure analyses revealed that the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe
with Sc concentrations of x = 0, 0.128, 0.153, and 0.193. The magnetic structure analyses revealed that the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O is a cone type whose base is in the ab plane and height is in the c-axis direction. The magnetic moments of Fe2(4
is a cone type whose base is in the ab plane and height is in the c-axis direction. The magnetic moments of Fe2(4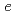 ), Fe4(4
), Fe4(4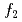 ), and Fe5(12
), and Fe5(12 ) are aligned with distinct angles, leading to the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe
) are aligned with distinct angles, leading to the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O , and can be explained by assuming that there is an antiferromagnetic superexchange interaction
, and can be explained by assuming that there is an antiferromagnetic superexchange interaction 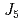 between Fe2(4
between Fe2(4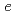 ) and Fe5(12
) and Fe5(12 ) that is negligible in the x = 0 crystal. The shorter bond distance of Fe2-O1 in Sc-rich crystals revealed by the crystal structure analyses enhances the superexchange interaction
) that is negligible in the x = 0 crystal. The shorter bond distance of Fe2-O1 in Sc-rich crystals revealed by the crystal structure analyses enhances the superexchange interaction 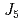 . The relatively strong
. The relatively strong 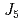 leads to competition among the three superexchange interactions,
leads to competition among the three superexchange interactions, 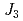 ,
, 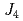 , and
, and 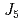 , resulting in the development of the helimagnetic structure. These findings facilitate the understanding of the essentials of the basic magnetic material BaFe
, resulting in the development of the helimagnetic structure. These findings facilitate the understanding of the essentials of the basic magnetic material BaFe O
O .
.
 Sc
Sc )
) O
O (0
(0  x
x  0.2) hexagonal ferrite
0.2) hexagonal ferrite丸山 建一*; 田中 誠也*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; 中尾 朗子*; 森山 健太郎*; 石川 喜久*; 天児 寧*; 飯山 拓*; 二村 竜祐*; 内海 重宣*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 892, p.162125_1 - 162125_8, 2022/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:16.86(Chemistry, Physical)Hexagonal ferrite Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O is an important magnetic oxide material in both science and engineering because it exhibits helimagnetism around room temperature (300 K). In this study, the magnetic phase diagram of Ba(Fe
is an important magnetic oxide material in both science and engineering because it exhibits helimagnetism around room temperature (300 K). In this study, the magnetic phase diagram of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O consisting of ferri-, heli-, antiferro-, and paramagnetic phases has been completed through magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements. The magnetic phase transition temperature to paramagnetism decreases with the increase in x, and the temperature at which the magnetization reaches a maximum, which corresponds to the magnetic phase transition from heli- to ferrimagnetism, is determined for low x crystals. The temperatures at which helimagnetism appears are precisely determined by observing the magnetic satellite reflection peaks in neutron diffraction at various temperatures, which characterize helimagnetism. Based on these results, the magnetic phase diagram of the Ba(Fe
consisting of ferri-, heli-, antiferro-, and paramagnetic phases has been completed through magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements. The magnetic phase transition temperature to paramagnetism decreases with the increase in x, and the temperature at which the magnetization reaches a maximum, which corresponds to the magnetic phase transition from heli- to ferrimagnetism, is determined for low x crystals. The temperatures at which helimagnetism appears are precisely determined by observing the magnetic satellite reflection peaks in neutron diffraction at various temperatures, which characterize helimagnetism. Based on these results, the magnetic phase diagram of the Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O system is constructed in the T-x plane. Helimagnetism appears at x
system is constructed in the T-x plane. Helimagnetism appears at x  0.06, and magnetism with antiferromagnetic components appears as the extension phase of helimagnetism at x
0.06, and magnetism with antiferromagnetic components appears as the extension phase of helimagnetism at x  0.19 through the coexistence region. The turn angle
0.19 through the coexistence region. The turn angle 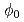 of the helix for each x crystal is calculated from the relationship,
of the helix for each x crystal is calculated from the relationship, 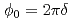 , where
, where  is the incommensurability. The turn angle
is the incommensurability. The turn angle 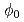 decreases with the increase in temperature for the same x crystal, and increases with the increase in x at the same temperature. Furthermore, it is found that there are clear thresholds at which
decreases with the increase in temperature for the same x crystal, and increases with the increase in x at the same temperature. Furthermore, it is found that there are clear thresholds at which 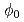 cannot take values between 0
cannot take values between 0 <
< 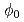 < 90
< 90 and 170
and 170 <
< 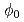 < 180
< 180 .
.
 K
K H(SeO
H(SeO )
)
鬼柳 亮嗣; 松尾 康光*; 大原 高志; 川崎 卓郎; 及川 健一; 金子 耕士; 田村 格良; 花島 隆泰*; 宗像 孝司*; 中尾 朗子*; et al.
no journal, ,
M H(XO
H(XO )
) (M=アルカリ金属、X=Se, S)で表わされる一連の物質群は比較的低温において高いプロトン伝導性を示すことが知られており、低い温度でも動作可能な電池やセンサーなどの応用材料として注目を集めている。高いプロトン伝導性は構造相転移とともに発現するが、その相転移温度はMやXの元素種によって変化する。本研究では元素種の変化によりなぜ相転移温度が変化するのかを明らかにするため、Mの元素としてRbとKを入れた物質を対象として相転移温度と内部構造の変化の関係を調べた。伝導度や示唆熱の測定により、K原子の濃度が濃くなるにつれて相転移温度が低下することが明らかとなったが、その変化はK原子の濃度に対して線形ではないことがわかった。中性子構造解析の結果、K原子は2つのMサイトのうちの一つを優先的に占有することがわかった。また、K原子の濃度が増えるにつれてSeO
(M=アルカリ金属、X=Se, S)で表わされる一連の物質群は比較的低温において高いプロトン伝導性を示すことが知られており、低い温度でも動作可能な電池やセンサーなどの応用材料として注目を集めている。高いプロトン伝導性は構造相転移とともに発現するが、その相転移温度はMやXの元素種によって変化する。本研究では元素種の変化によりなぜ相転移温度が変化するのかを明らかにするため、Mの元素としてRbとKを入れた物質を対象として相転移温度と内部構造の変化の関係を調べた。伝導度や示唆熱の測定により、K原子の濃度が濃くなるにつれて相転移温度が低下することが明らかとなったが、その変化はK原子の濃度に対して線形ではないことがわかった。中性子構造解析の結果、K原子は2つのMサイトのうちの一つを優先的に占有することがわかった。また、K原子の濃度が増えるにつれてSeO 四面体のひずみが大きくなっていることがわかり、この歪が相転移温度の決定に大きな役割を果たしていることが示唆された。
四面体のひずみが大きくなっていることがわかり、この歪が相転移温度の決定に大きな役割を果たしていることが示唆された。
鬼柳 亮嗣; 石川 喜久*; 大原 高志; 森山 健太郎*; 宗像 孝司*; 中尾 朗子*; 坂倉 輝俊*; 木村 宏之*
no journal, ,
SENJUは、J-PARCの物質生命科学実験施設(MLF)の単結晶中性子回折計である。本研究では、強吸収体における定量的な構造解析の可能性について研究を行った。結果、測定法や測定データの取り扱いを工夫することにより、定量的な構造解析が強吸収体においても可能であることが示された。
鬼柳 亮嗣; 大原 高志; 中尾 朗子*; 宗像 孝司*; 石川 喜久*; 森山 健太郎*; 中村 龍也; 金子 耕士; 田村 格良
no journal, ,
J-PARC/MLFのBL18に設置されているTOF-Laue型中性子単結晶構造解析装置SENJUは、無機物質や小型の分子性結晶,磁性体の磁気構造解析などを主なターゲットとした装置である。J-PARC/MLFで発生する大強度の白色中性子と広い立体角をカバーする検出器により、小さな試料でも効率的に逆空間を測定できることがSENJUの特徴であり、これまで多くのユーザー実験を行うとともに、装置の高度化を進めてきた。SENJUでは主に円筒形に配置された37台の2次元検出器により広い立体角のカバーが実現されているが、特殊環境下での測定など、試料の回転軸が1つしかない場合は測定領域が限定されてしまうことが問題であった。そこで、従来型の検出器よりも薄くコンパクトな検出器を開発し、試料の斜め下の位置にも検出器を追加設置した。これによりカバーする立体角が約10%増加し、1度に測定できる領域が広がるとともに、より高効率な測定を行うことが可能となった。また、ユーザーが実験終了後に各所属大学等でもスムーズな解析が行えるように、解析ソフトのonline化を行った。これはクラウド上にデータを保管し、webアプリ化したソフトをブラウザ上で使うことにより、SENJUのデータ解析をユーザー自身のPC上に解析環境を構築することなく行えるようにするものである。その他、測定効率の向上にむけた複数結晶の同時測定や3次元全散乱解析について報告する。
鬼柳 亮嗣; 大原 高志; 中尾 朗子*; 宗像 孝司*; 石川 喜久*; 森山 健太郎*
no journal, ,
J-PARC MLFに設置されている単結晶構造解析装置SENJUでは無機物や低分子化合物などの結晶/磁気構造解析を行なっている。構造解析では、測定されたデータからBragg反射強度を抽出したものを入力データとして使われるが、実際に測定されるデータには試料環境装置からの散乱などが含まれていることがあるため、1つ1つのBragg反射データを確認する必要がある。しかしながら、数千から数万に上る大量のデータを手作業でチェックするのは現実的には難しいため、効率的なデータチェックの実現に向けて、機械学習の適用を試みた。機械学習としては「教師あり学習」と「Autoencoder」による学習を行なった。「教師あり学習」では、反射が孤立して存在する「良いデータ」と反射近傍に余計な回折線などが存在する「悪いデータ」からなる教師データを用いて学習を行い、「Autoencoder」では「良いデータ」のencodeを学習した。「教師あり学習」の訓練では高い正答率が実現され、実データに対しても同程度の正解率が得られた。また、Autoencoderの結果も同様な結果が得られ、現状では、わずかながらAutoencoderの方が良い働きをすることが示された。